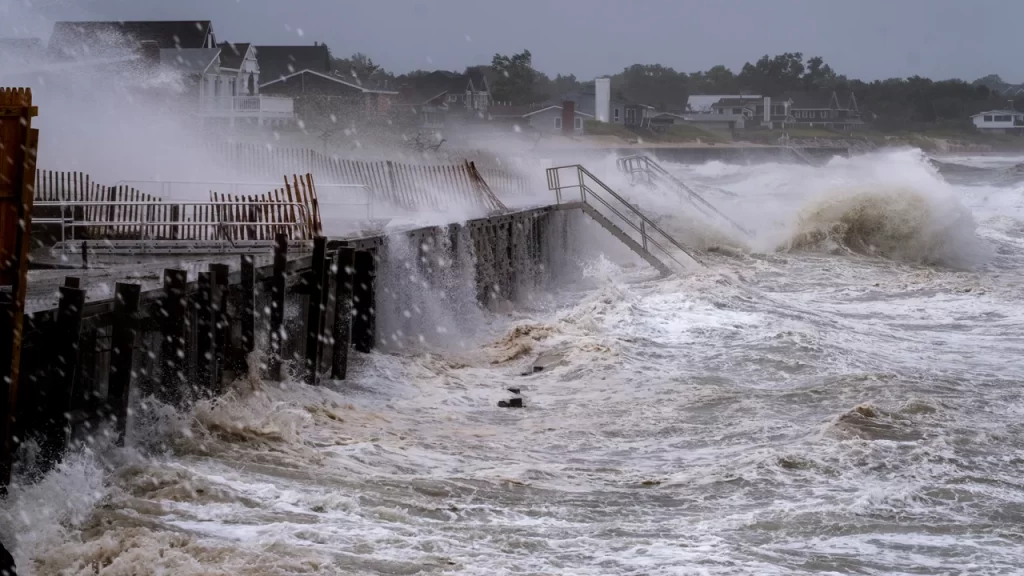
Flooding is a devastating natural disaster that can wreak havoc on communities, causing immense damage to properties and posing significant health risks. While the immediate dangers of flooding are evident, the impact on respiratory health is often overlooked. Floodwaters can introduce a plethora of harmful substances and pathogens, leading to a range of respiratory issues. In this blog, we will delve into the potential respiratory health harms following flooding and provide essential steps to protect and restore respiratory well-being during the recovery process.
Understanding the Respiratory Risks of Flooding
Floodwaters can become contaminated with a variety of hazardous substances, including sewage, chemicals, and debris. As these waters recede, they leave behind a host of respiratory irritants that can affect both indoor and outdoor environments. Common respiratory hazards after flooding include:
- Mold Growth: Standing water and high humidity provide ideal conditions for mold growth, leading to allergenic and irritative respiratory issues.
- Airborne Particulates: Floodwaters can stir up dust, debris, and pollution, increasing the concentration of airborne particulates that may exacerbate respiratory conditions.
- Bacterial and Viral Contamination: Contaminated floodwaters may carry harmful bacteria and viruses, which can cause respiratory infections and exacerbate existing respiratory conditions.
- Chemical Exposure: Floodwaters can mix with chemicals from industrial sites or household products, releasing toxic fumes that pose respiratory risks.
Steps to Protect Respiratory Health After Flooding
During the recovery phase following flooding, it is crucial to take specific measures to safeguard respiratory health. Here are vital steps to consider:
Limit Exposure During Cleanup
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as masks, gloves, and goggles when cleaning up flood-damaged areas to minimize inhalation of harmful substances.
Ventilate and Dehumidify Indoor Spaces
Open windows and use fans to improve indoor air circulation and reduce moisture, inhibiting mold growth. Utilize dehumidifiers to maintain optimal humidity levels.
Clean and Disinfect Thoroughly
Thoroughly clean and disinfect surfaces to remove potential contaminants, using safe and effective cleaning agents.
Avoid Indoor Mold Exposure
If mold is present, hire professionals trained in mold remediation to safely remove it and prevent further spread.
Monitor Air Quality
Stay informed about air quality in your area, and avoid outdoor activities during times of high pollution or poor air quality.
Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to keep your respiratory tract moist and to help your body expel pollutants.
Seek Medical Attention
If you experience respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath, seek medical attention promptly.
Prevent Future Flooding
Take preventive measures to protect your property from future flooding, such as installing flood barriers or elevating electrical outlets and appliances.
Focus on Respiratory Hygiene
Practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing, to reduce the spread of respiratory infections.
Promote Community Awareness
Advocate for community awareness regarding respiratory health after flooding and the importance of taking precautionary measures.
Conclusion
The impact of flooding extends beyond visible damages to encompass serious risks to respiratory health. By understanding and addressing the potential respiratory hazards, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities during the flood recovery process. Timely and proactive measures such as proper cleaning, mold prevention, and staying informed about air quality can help mitigate respiratory health harms and foster a safer and healthier environment for all.